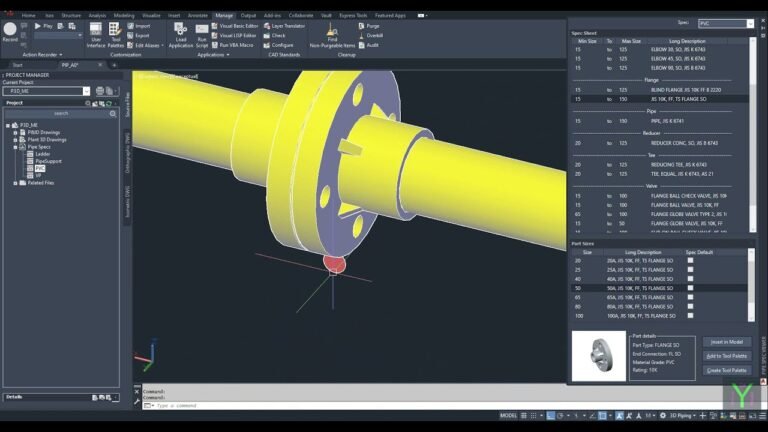
In the realm of industrial piping design, Autodesk’s Plant 3D stands out as a powerful tool for creating intelligent 3D models of piping systems. Among its many features, the Threaded Pipe Spec Editor is crucial for defining specifications and ensuring accuracy in the design process. One particular challenge designers often face is working with unfixed length threaded pipes. This article delves into the intricacies of handling unfixed length threaded pipes within Plant 3D, highlighting the significance of this feature, its applications, and best practices for using the Threaded Pipe Spec Editor.
What is Plant 3D?
Autodesk Plant 3D is a comprehensive solution for designing, modeling, and documenting process plant projects. It facilitates the creation of detailed 3D models that integrate seamlessly with P&IDs (Piping and Instrumentation Diagrams) and other project documentation.
Key Features of Plant 3D:
- Intelligent Piping Design: Automates the creation of piping systems, complete with fittings, valves, and instruments.
- Comprehensive Spec Editor: Enables the creation and management of piping specifications to ensure design consistency and compliance.
- Integrated Collaboration: Supports multi-user workflows, enhancing collaboration among teams.
Understanding the Threaded Pipe Spec Editor
What is the Threaded Pipe Spec Editor?
The Threaded Pipe Spec Editor in Plant 3D allows users to define plant 3d threaded pipe spec editor unfixed length and manage the specifications for threaded piping components. These specifications dictate the types of pipes, fittings, and materials used in a project, ensuring that designs adhere to project requirements and industry standards.
Why is the Spec Editor Important?
- Standardization: Ensures all components in a piping system adhere to specified standards, reducing errors and inconsistencies.
- Customization: Allows users to define custom specifications tailored to unique project needs.
- Efficiency: Streamlines the design process by automating the selection of compatible components based on predefined specs.
Handling Unfixed Length Threaded Pipes
What are Unfixed Length Threaded Pipes?
Unfixed length threaded pipes refer to pipe segments whose lengths are not predetermined in the specification. This flexibility is essential in scenarios where:
- Field Adjustments: Exact pipe lengths are determined on-site due to space constraints or installation challenges.
- Customization: Projects require custom-length pipes that do not conform to standard length increments.
Challenges with Unfixed Length Pipes
- Accuracy in Modeling: Ensuring the virtual model accurately represents the final installation.
- Spec Management: Maintaining clear documentation and specifications for custom-length pipes.
- Material Estimation: Calculating material requirements and costs accurately.
Configuring Unfixed Length Pipes in the Spec Editor
- Defining Custom Lengths:
- Open the Threaded Pipe Spec Editor in Plant 3D.
- Navigate to the desired pipe spec and select the threaded pipe category.
- Enable the option for unfixed or custom lengths, allowing you to input specific dimensions as needed.
- Specifying Threaded Connections:
- Ensure that the threaded connections are properly configured to accommodate variable pipe lengths.
- Define the thread type (e.g., NPT, BSP) and ensure compatibility with fittings and valves.
- Validation and Testing:
- Use the spec editor’s validation tools to check for any inconsistencies or errors.
- Test the spec in a sample model to ensure that unfixed lengths are correctly implemented.
Best Practices for Using Unfixed Length Pipes
1. Collaborate with Field Teams
- Maintain open communication with field engineers and installers to gather accurate measurements and requirements.
- Update the spec based on real-time feedback from the field.
2. Document Custom Lengths
- Clearly document all instances of unfixed length pipes in the project documentation.
- Include detailed notes and diagrams to guide installation teams.
3. Leverage Plant 3D Features
- Utilize Plant 3D’s reporting tools to generate accurate bills of materials (BOMs) that reflect custom lengths.
- Take advantage of the software’s clash detection and validation features to avoid potential issues during installation.
4. Regularly Update Specifications
- Review and update the piping specs regularly to incorporate lessons learned and feedback from completed projects.
- Ensure all team members are using the latest version of the spec to maintain consistency.
Conclusion
The ability to handle unfixed length threaded pipes in Autodesk Plant 3D’s Threaded Pipe Spec Editor provides designers with the flexibility needed to tackle complex piping projects. By understanding how to configure and manage these specifications, teams can enhance their design accuracy, streamline workflows, and ensure successful project outcomes. Leveraging the full capabilities of Plant 3D, including its spec editor, not only simplifies the design process but also ensures that projects meet the highest standards of quality and precision.